

The server name can be a NetBIOS machine name or an IP/FQDN address (IPv4 as well as v6 are supported).

A server or host name, which is prefaced by \\.Universal naming convention (UNC) paths, which are used to access network resources, have the following format:
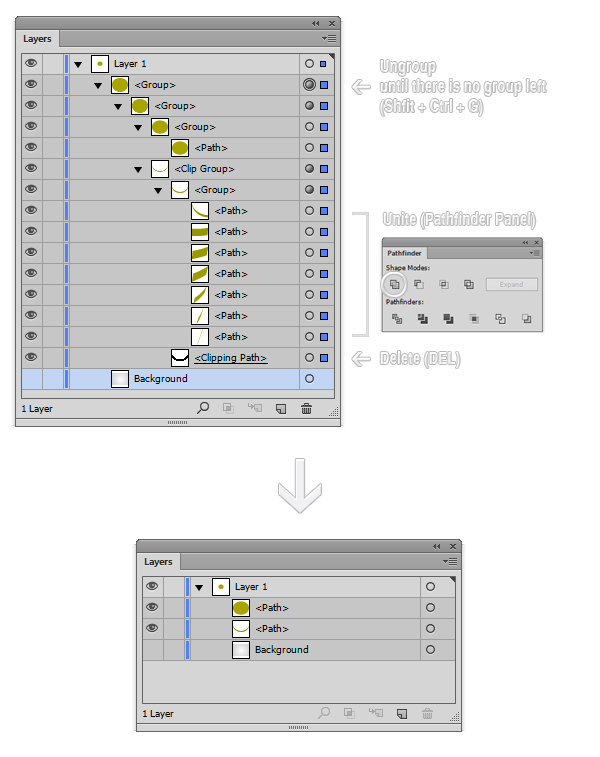
G CLIP PATH ON TOP OF OTHER G CODE
If you would like to see code comments translated to languages other than English, let us know in this GitHub discussion issue. ' The subprocess displays the following output: ' Launching again, after setting current directory to D:\FY2018 ' Current directory is 'C:\Programs\file-paths' ' The example displays the following output: using System Ĭonsole.WriteLine($"Current directory is '")Ĭonsole.WriteLine("Press any key to continue. It assumes that the directory D:\FY2018\ exists, and that you haven't set any current directory for D:\ from the command prompt before running the example. The following example illustrates the difference between absolute and relative paths. ) and still be fully qualified if the resolved path always points to the same location. Note that such a path can include relative directory segments (. You can determine whether a file path is fully qualified (that is, it the path is independent of the current directory and does not change when the current directory changes) by calling the Path.IsPathFullyQualified method.
G CLIP PATH ON TOP OF OTHER G WINDOWS
Use of the second form when the first is intended is a common source of bugs that involve Windows file paths. As result, the first is an absolute path from the root directory of drive C:, whereas the second is a relative path from the current directory of drive C. Both specify the optional volume specifier ( C: in both cases), but the first begins with the root of the specified volume, whereas the second does not. Note the difference between the last two paths. \Program Files\Custom Utilities\StringFinder.exeĪn absolute path from the root of the current drive.Ī relative path to a file in a subdirectory of the current directory.Ī relative path to file in a directory that is a peer of the current directory.Īn absolute path to a file from the root of drive C.Ī relative path from the current directory of the C: drive. PathĪn absolute file path from the root of drive C. The following table shows some possible directory and file paths. Otherwise, the path is relative to the current directory. If no volume or drive letter is specified and the directory name begins with the directory separator character, the path is relative from the root of the current drive. If all three components are present, the path is absolute. The directory separator character separates the file path and the filename. The directory separator character separates subdirectories within the nested directory hierarchy.

This topic discusses the formats for file paths that you can use on Windows systems. This path is then passed to Windows file system APIs. Members of many of the types in the System.IO namespace include a path parameter that lets you specify an absolute or relative path to a file system resource.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
